By Chris Tilley
There are so many things to talk about in the Arctic that I am going to limit this article to the sea ice. The National Snow and Ice Data Center has excellent information on the Arctic including an excellent application for viewing the extent of arctic ice and daily updates. The information comes from a variety of satellites that have been collecting data since 1979.
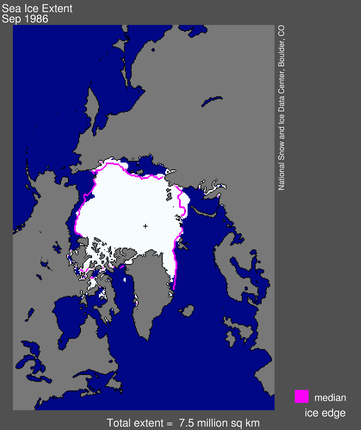


(Source, National Snow and Ice Data Center)
The above three images show the ice extent in September of 1986, 2007 and 2009. The 2007 was the lowest on record.(Source) . September has the least amount of sea ice in a year. Below is a graph show sea ice extent for January from 1979 to 2010. That is not a good trend.
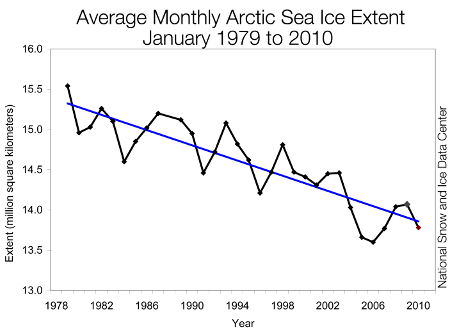
(Source, National Snow and Ice Data Center)
The other consideration is how thick the ice is and they measure that as well. Between 1950 and 1999 the ice draft,that is the amount in the water shrunk from and average of 3m to 1.6m. A NASA study from 2004 to 2008 saw the overall thickness decrease an average of .17m each year.
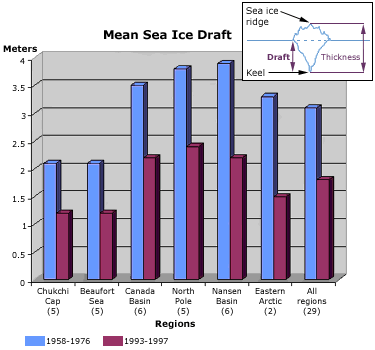
(Source, National Snow and Ice Data Center)
So what does this all mean. First this ice is already floating on the ocean so its melting will not affect sea levels. It has to be ice on land such as Greenland and Antarctica to affect sea levels for more on this see our previous article ‘Melting Ice‘ . The biggest change is going from something white to something dark. As we loose ice more of the ocean is going to be visible and dark things absorb more energy from the sun that white things. I saw an example of this up skiing, A small pine bow in the sun slowly melting a hole in the snow. You can see examples of this in your environment, put your hand over a light colored vehicle and a dark one or over concrete and asphalt. The darker one will be hotter.
Another effect is there is going to be more shipping up there as it will be possible to get ships through without ice breakers. For the first time two German ships used the Northeast Passage to go from South Korea to the Netherlands. I shave 10 days from their travel time and cut their distance by 25%.
“I think it will soon be possible to navigate the Northeast Passage all year round. We were escorted by an ice-breaker but, frankly, we could have done without it. This is great news for our industry.”(Source)
Canada and the US are both putting deep water ports and bases in the Arctic to patrol the Northwest Passage.(Source) There are resources up there including oil and gas and there is dispute over who owns what. Now that these resources are becoming available its going to get interesting.

(Source, Wikipedia)
Probably the face of climate change in the Arctic is the Polar Bear. Eight of nineteen subpopulations are declining, one is increasing, three are stable and the rest don’t have enough data. The bears hunt off of the ice so the reduction of ice is reducing their ability to hunt. There have also been cases of Polar bears drowning trying to find food. The bears are excellent swimmer and have been observed up 200 miles from land.(Source)
The Arctic is where we can see climate change happening. Its an area that we will hear more and more about over the coming years.













